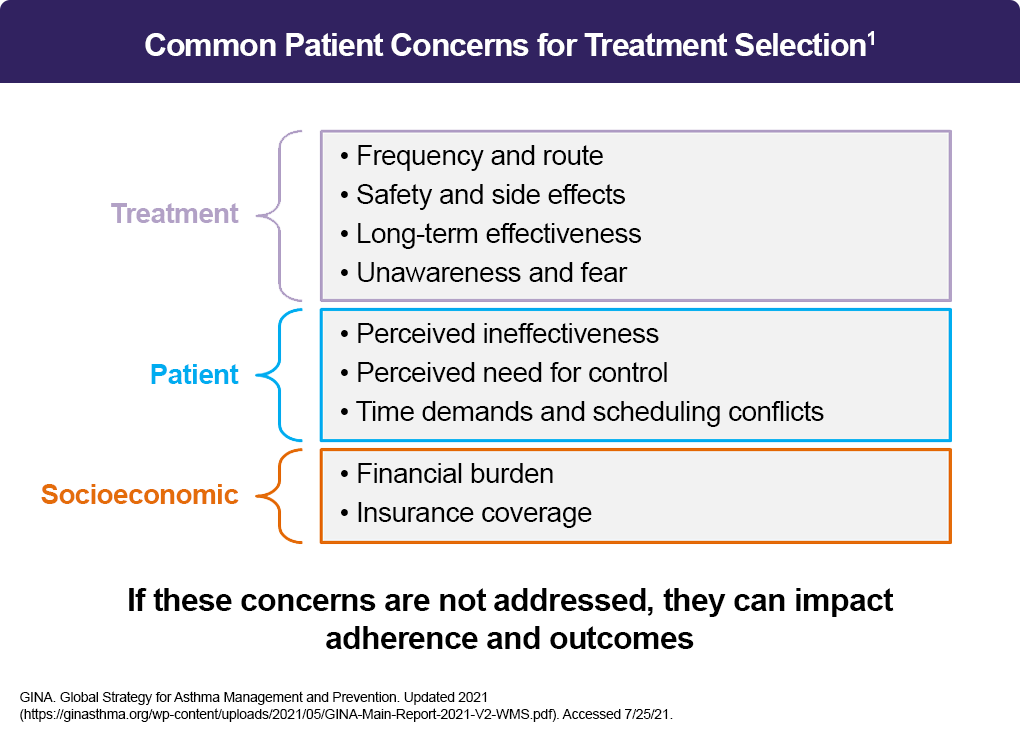
Barriers to Treatment
In the management of severe asthma, patients should be assessed for potential barriers to treatment including the economic, physical, mental, emotional, and social burden imposed by this condition. Considerations of medication-related adverse events, which may be a barrier to continued treatment, should also be assessed, as well as potential comorbidities, drug interaction, and inhaler technique. In addition, patients with severe asthma may have a tendency toward overuse of short-acting inhaled therapy, and should be regularly assessed for poor long-term control of symptoms.1
Reference:
- Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. Updated 2021 (https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/GINA-Main-Report-2021-V2-WMS.pdf).
